LLM Conversation Branching on GPT, Gemini, Claude Native Interfaces vs. Cognis Ai
Most AI chats still run in a straight line: prompt, answer, prompt, answer. When you want a new direction, you often restart and rebuild context. That’s the friction LLM conversation branching removes.
One chat becomes a tree, with a stable trunk and many paths. In practice, you create branch conversations to test alternatives side by side. You keep the best result and discard the rest. This is nonlinear prompting with structure. It’s not just “more messages.” The payoff is practical.
You get clearer context memory and fewer wrong turns. Branching also gives you a record of how decisions happened. That’s why the chat GPT branch feature is often treated like version control for AI chat.
In today’s guide, you’ll learn what branching is, how it works, why it helps, and how to leverage branching for your benefit. You’ll also see why LLM conversation branching is increasingly treated as a workflow primitive, not a novelty.
What Is Chat Branching (and How It Differs From Normal Chat)?
Chat branching is the ability to fork a conversation at a specific message into a new, independent thread, while inheriting all context up to that split.
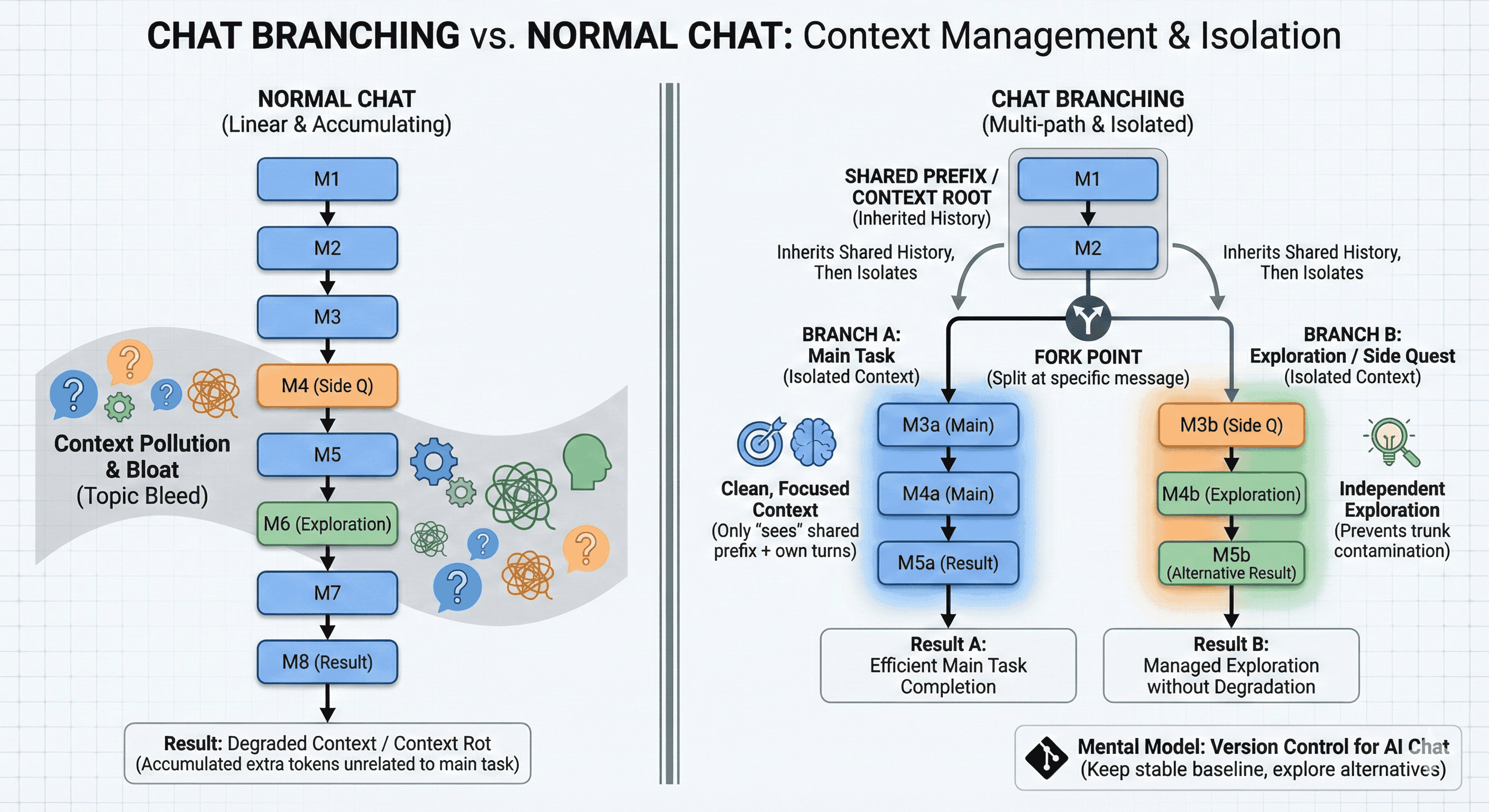
Chat Branching vs. Single Chat
Linear vs. multi-path
A normal chat is a single lane. As you troubleshoot and explore side questions, the transcript accumulates extra tokens that don’t serve the main task. That bloat can become context pollution and eventually context rot..
Branching changes the structure. Each fork shares the same roots and then stays isolated afterward. That isolation improves context memory because each path only “sees” the shared prefix plus its own turns.
Context inheritance vs. isolation
A branch inherits the shared history before the split. After the split, it stays separate. This supports context isolation in LLMs and reduces topic bleed.
The version-control framing
A useful mental model is version control for AI chat: keep a stable baseline, then explore alternatives as separate paths you can compare. Research framed as ContextBranch formalizes this with primitives and shows why the chat GPT branch feature can reduce wasted effort.
Done intentionally, LLM conversation branching also helps manage multi‑turn conversation degradation by preventing unrelated explorations from contaminating the trunk.
Why Conversation Branching Matters: Human-Aligned Thinking and Better Outputs
People don’t think in straight lines. We revisit assumptions, test “what-if” paths, and compare options. If you want a quick mental model: branching helps you think in alternatives first, then converge. That convergence step is where teams save time, reduce duplicate work, and produce outputs that feel more consistent.
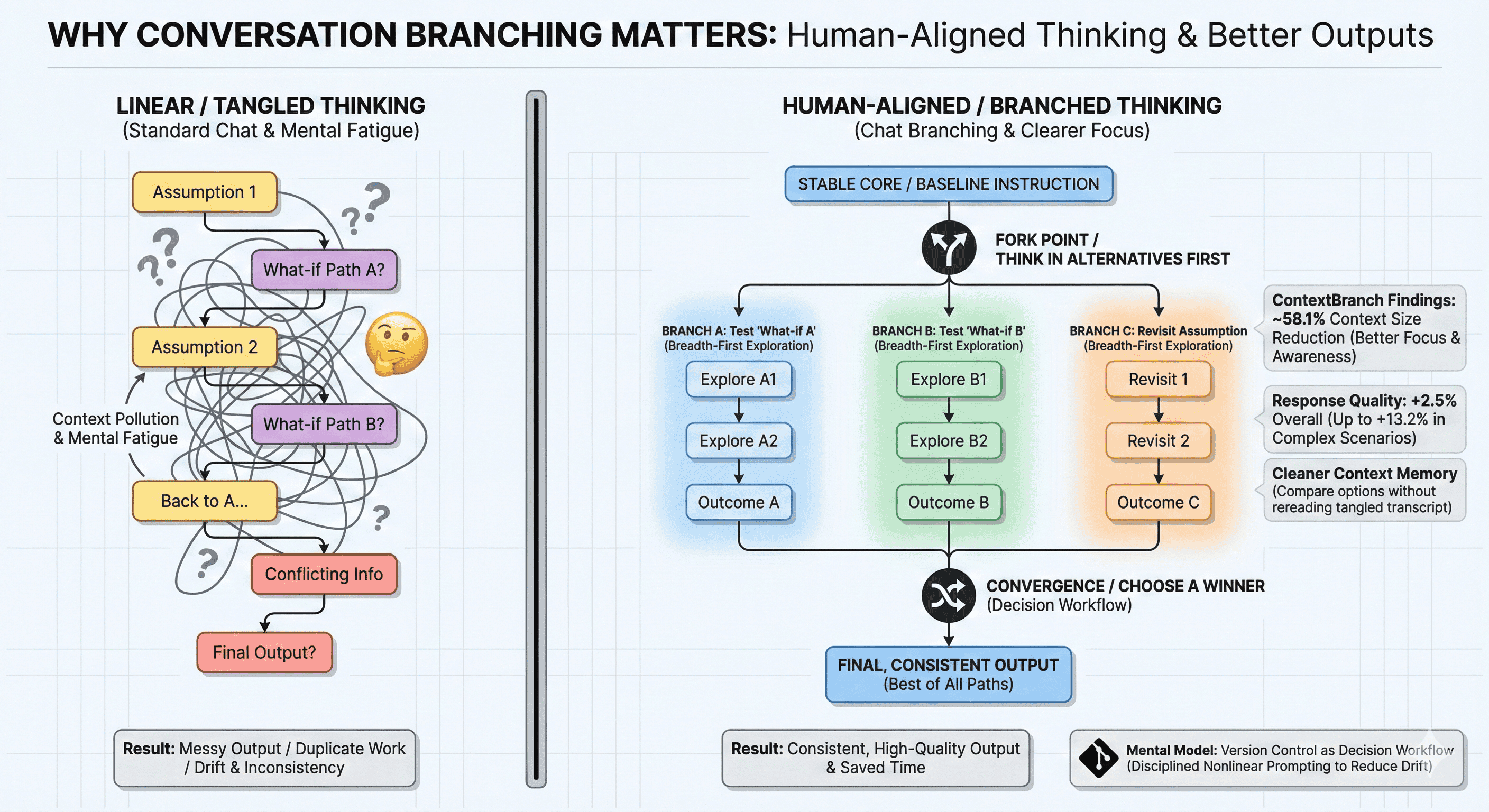
Why LLM Conversation Branching Matters
People don’t think in straight lines. We revisit assumptions, test “what-if” paths, and compare options. If you want a quick mental model: branching helps you think in alternatives first, then converge. That convergence step is where teams save time, reduce duplicate work, and produce outputs that feel more consistent.LLM conversation branching fits real work. It lets you explore breadth-first, without corrupting a baseline. Your brief cites ContextBranchfindings with measurable gains. Response quality improves by ~2.5% overall, and up to 13.2% in complex scenarios
It also reports context-size reductions around ~58.1%. That improves focus and context awareness. The practical outcome is cleaner context memory. You can compare options without rereading a tangled transcript.
Branching also changes how you instruct models. Instead of layering conflicting instructions, you keep the core stable. This is the operational meaning of the advantages of conversation branching. You create branch conversations, then choose a winner.
With disciplined nonlinear prompting, you keep experiments comparable. You also reduce drift that can worsen multi‑turn conversation degradation. That’s when the chat GPT branch feature becomes a decision workflow. And that’s when version control for AI chat stops being a metaphor.
Cognis Ai’s True Multi-LLM, Infinite-Branch Workspace
Cognis AI is designed for teams who want branching to feel like a real workspace, not a pile of disconnected threads.
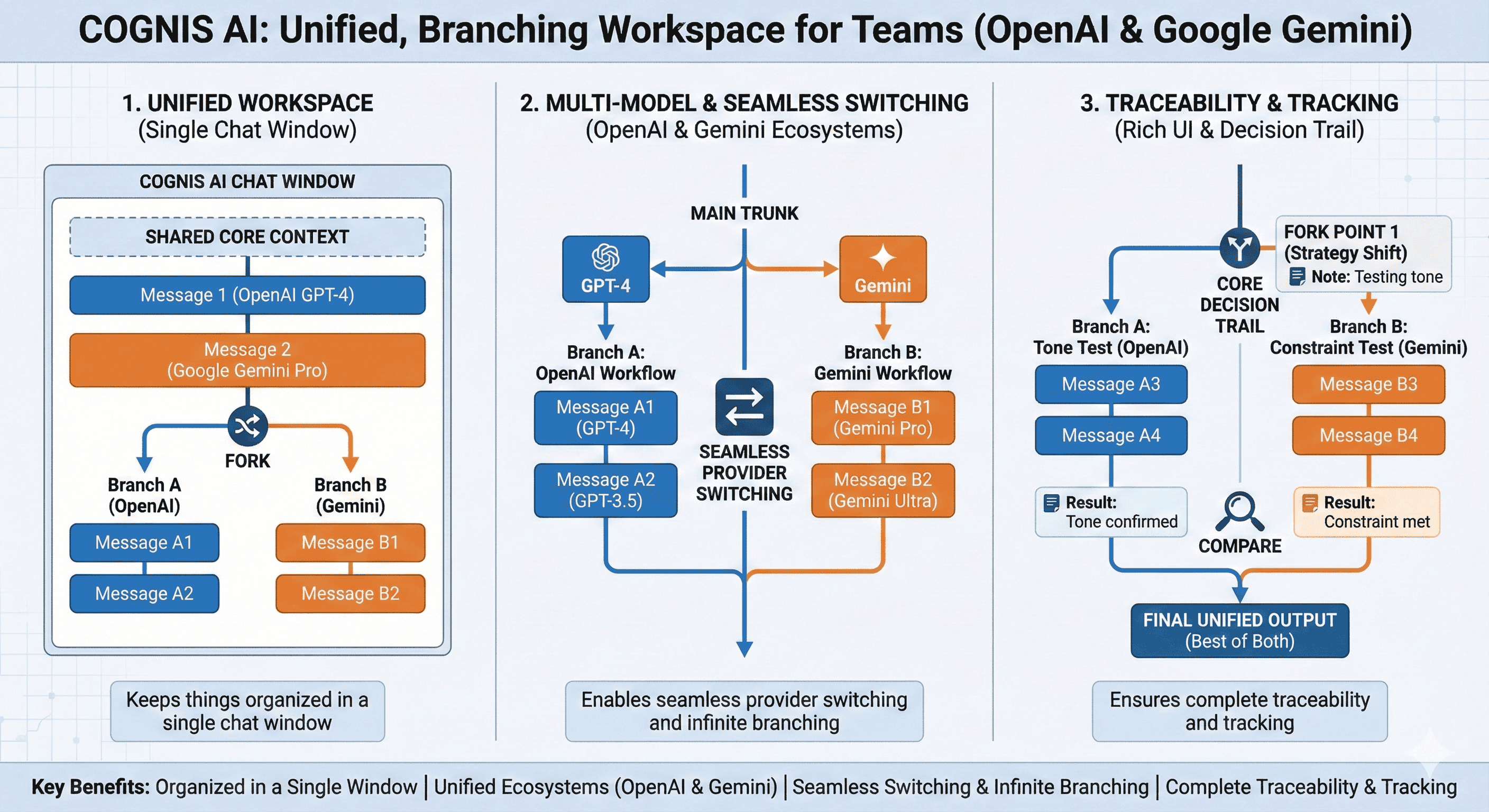
LLM Conversation Branching in Cognis Ai
Cognis AI brings together all OpenAI models and Google Gemini models into a single chat window. You can switch between models from different providers seamlessly while creating infinite branches and sub-branches with complete traceability and tracking through a rich UI.
That matters because comparison workflows are where branching either stays organized or turns into scattered tabs. Cognis AI keeps the tree visible and navigable so experiments can be revisited and audited.
For example:If you’re comparing results from Gemini versus other outputs, Cognis AI keeps the shared core intact.
If you’re comparing outputs from Gemini AI across subtasks, Cognis AI keeps those branches connected to the same core message.
If you’re evaluating ChatGPT vs Gemini or running a Google Gemini vs ChatGPT workflow, Cognis AI keeps the decision trail unified while you switch models.
Cognis AI combines ease of use and advanced memory management unlike any other available tool, via:
- Keeping things organized in a single chat window
- Unifying OpenAI and the Google Gemini ecosystems
- Enabling seamless provider switching and infinite branching
- Ensuring complete traceability and tracking
Branching on ChatGPT vs. Claude vs. Google Ai Studio vs. Cognis Ai
Branching on GlobalGPT vs. TypeMind vs. T3.Chat vs. Cognis Ai
Model aggregators often aim to reduce friction across models, but branching can still feel inconsistent. The key questions are: can you branch cleanly, see the tree, navigate fast, and keep experiments traceable?
In a true branching workflow, LLM conversation branching is not just a retry button. It’s a structured tree where branched conversations remain connected to their parent branches.
Real‑World Use Cases: How Teams Use LLM Conversation Branching
Risks of Branching and How Cognis Ai's Unified Interface Mitigates Risk Exposure
Branching is useful, but it brings new problems once you start using it every day.
Risk one is sprawl. Too many forks turn into clutter, and you waste time choosing between half-finished paths.
There are limits too. Context caps are real, and you can’t “undo” them, and running many branches costs more compute. That’s why LLM conversation branching needs restraint. It’s also why the interface matters. One simple anti-sprawl rule is a branch limit per decision. Explore a few serious options, then merge and move on.
Risk two is inconsistency. Every branch copies the starting context, including old or wrong assumptions.
To reduce inconsistency, keep the shared context short and precise. If the base is wrong, every branch is wrong in the same way.
Risk three is privacy. Sensitive details in the shared context can get duplicated across many forks.
To reduce privacy exposure, check what’s inside the shared context before creating new branches.
Cognis AI’s approach is to keep branches and sub-branches clearly linked to their parent threads. The UI keeps them easy to follow and easy to audit.
Cognis also keeps model switching inside the same chat thread. That reduces switching overhead, prevents confusion, and avoids losing quality across long multi-turn conversations. Used properly, Cognis AI makes branching feel structured, not messy.
Future Evolution: Visualization, Selective Merging, Agents, and Multimodal Workspaces
Branching is already useful, and it’s going to get more useful in a few clear ways.
- It’ll become more visual. Instead of long scrolls, you’ll be able to see the whole conversation as a map. That makes it easier to understand where things split and why.
- Merging will improve. Right now, combining two branches usually means copy-paste. In the future, you’ll be able to bring back only the specific points you want, not entire blocks of text.
- The system will suggest branching automatically. If your chat starts going in two directions, the tool will nudge you to split it so things stay organized.
- Different branches may use different models. One branch might use a model better at writing, another better at reasoning, another better at coding — depending on what you're doing.
- Branching will move beyond text. It won’t just be chat threads. It’ll become a workspace where you can branch with images, notes, tables, and diagrams on the same canvas.
Overall, branching will feel less like managing multiple chats, and more like navigating a structured workspace. And merging back the useful parts will become a normal step in the process.
Frequently Asked Questions
In practice, people often edit an earlier message and use an action like the ChatGPT branch in a new chat to explore an alternate path.
They are parallel paths from the same baseline that remain independent after the split.
It reduces duplicate effort by letting you explore alternatives from the same baseline without copy-paste. It also creates a clearer decision trail because you compare outcomes side by side.
Normal chat is one lane, so detours pile up. Branching isolates detours into separate paths, preventing context pollution and topic bleed.
You compare alternatives side-by-side while keeping the baseline clean. Less drift, fewer wrong turns, and clearer instructions per path.
Fork when direction changes, label the branch by intent (tone/constraint/audience), add a note, compare outputs, then converge on one winner.
Native tools split into messy threads and single ecosystems. Cognis keeps the full tree visible, supports infinite branches, and lets you switch models/providers cleanly.
External References
- Zang et al., (2025). A Survey on Parallel Reasoning. Read here.
- Building Autonomous, Resilient, and Intelligent Agentic AI Systems. Infosys Foundation. Read here
- Zhou et aL. (2025). CARD: A Cache-Assisted Parallel Speculative Decoding Framework via Query-and-Correct Paradigm for Accelerating LLM Inference. Read here
- B. C. Nanjundappa & S. Maaheshwari (2025). Context Branching for LLM Conversations: A Version Control Approach to Exploratory Programming. Read here.
- K. Salahi & P. Gurusankar (2025). More Effectively Searching Trees of Thought for Increased Reasoning Ability in Large Language Models. Stanford University. Read here
AI Innovation
Generative AI
LLM
Contact Us
Fill up the form and our team will get back to you within 24 hrs
